Asset theft is top economic crime in China
Updated: 2014-02-28 02:17
(China Daily)
|
|||||||||||
China's economic crime rate may be lower than that of the world, but many companies in the Chinese mainland are extremely concerned about bribery, corruption and procurement fraud, according to a PwC survey released on Thursday.
The analysis is based on responses from more than 5,000 executives from 95 countries and regions, including 85 in the Chinese mainland and 116 in Hong Kong and Macao, and given during the past 24 months.
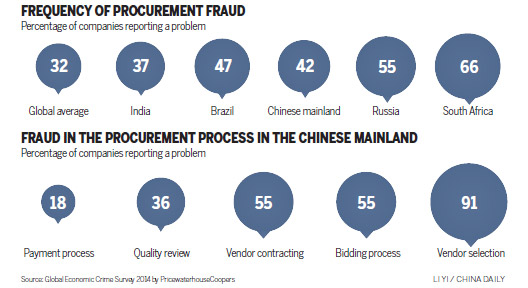
The report said 27 percent of mainland respondents and 16 percent from Hong Kong and Macao said they had been victims of economic crime, compared with 37 percent globally and 32 percent in Asia Pacific.
But a reduced capability among mainland-based organizations to detect economic crime could partly explain the results.
Asset misappropriation in China was the largest type of fraud reported, which was in line with global results.
In the mainland, procurement fraud came second, as reported by respondents who said their organizations had suffered economic crime.
It was closely followed by bribery and corruption in the mainland, and money laundering and cybercrime in Hong Kong and Macao.
"Two recurring themes featured heavily in the Chinese mainland within the survey: concern about bribery and corruption and that of procurement fraud and kickbacks," said John Donker, a Hong Kong-based partner at PwC China who was responsible for the survey.
About 39 percent of mainland respondents who said they were crime victims said they had experienced bribery and corruption, and 41 percent predicted that it would increase.
Respondents in the mainland said they were five times more likely to be asked to pay a bribe than respondents in Hong Kong and one-and-a-half times likelier than regional and global averages.
Their concern about bribery and corruption were said to stem partly from the ongoing anti-corruption drive on the mainland, which has resulted in disciplinary measures against officials nationwide and involved multinational corporations and their foreign executives. "We have already seen China government's increasing efforts to address this," Donker said.
Procurement fraud was identified by mainland respondents as one of the most frequently experienced economic crimes, with 48 percent of respondents suffering economic crimes saying they encountered it mainly during stages of vendor selection, contracting and bidding process. The figure was significantly higher than the global result of 29 percent.
The survey also showed that in almost four out of every five economic crimes reported in the Chinese mainland, the perpetrator was identified as someone inside the company and that 28 percent of these perpetrators were under the age of 30.
"The prevalence of internal economic crime themes suggests that many organizations in China need to continue to focus effort on implementing and enforcing internal controls," Donker said.
"They need to address a lack of organizational transparency and ensure that they monitor suppliers and employee relationships."
The data-dependent businesses in Hong Kong, combined with the rapid growth of social media, underscore the growing threat posed by cybercrime. In Hong Kong and Macao, 37 percent of respondents said they had been victimized by cybercrime.
In addition, 99 percent of respondents said that the risk of cybercrime has remained at a steady level or increased.
"Ultimately, cybercrime is not strictly a technology problem but a strategy problem, a people problem and a process problem," said Ramesh Moosa, a partner at PwC China.
"Organizations are not being attacked by computers but by people attempting to exploit human frailty as much as technical vulnerability," he pointed out.
The survey also found that 37 percent of Hong Kong and Macao respondents had encountered money laundering, three times more than regional and global averages.
"The concentration of financial services businesses in Hong Kong and risks faced by Macao's large gaming sector, combined with increased local and global regulatory activity, makes this a significant area of future focus," said Donker.
Related Stories
Reaffirm China's resolve to fight corruption 2014-02-27 07:18
Judicial corruption targeted 2014-02-25 08:15
China targets judicial corruption in commutation 2014-02-24 17:10
To stop corruption you first need to swat flies 2014-02-21 08:31
China's network against corruption 2014-02-20 16:14
CNN: Corruption as China's top priority 2014-02-20 14:59
Today's Top News
Armed men seize govt HQ in Ukraine's Crimea
Xi looks to a nation of cyberpower
UK, Germany at odds on EU reform
Asset theft is top economic crime
New Ukraine ministers proposed
Attemped attacks on chemical convoy
Guitarist Paco de Lucia dies
US senators scold Swiss bank in tax spat
Hot Topics
Lunar probe , China growth forecasts, Emission rules get tougher, China seen through 'colored lens', International board,
Editor's Picks

|

|

|

|

|

|





