A country at the opera
Updated: 2013-10-18 00:23
By Raymond Zhou (China Daily)
|
|||||||||||
|
 |
|
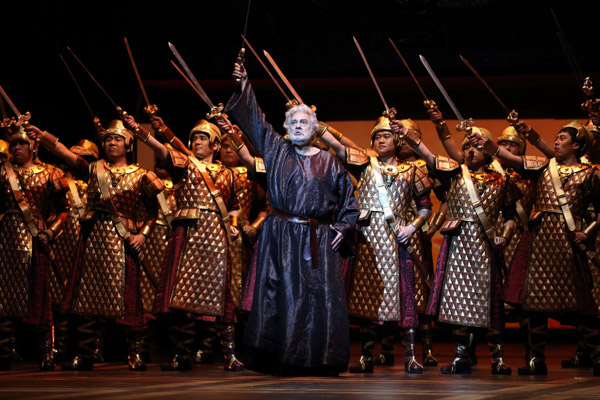
Opera superstar Placido Domingo plays the title role for Nabucco at the National Center for the Performing Arts in Beijing. Provided to China Daily |
Verdi in China
 |
| Verdi |
But that is inaccurate. According to Liu Shirong, an eminent music scholar, there are historical records that chronicle performances of Western music, including opera, in the Chinese cities of Shanghai and Harbin. For example, La Traviata was presented in Harbin in 1924, followed by Aida. These were all touring productions from Western countries, serving almost exclusively the expatriate communities in these Chinese cities. Liu was certain that Beijing and Tianjin, also with enclaves of Western residents, saw performances of Western opera as well, but records have been lost. And Hong Kong must have been exposed to it earlier than the rest of China, adds Liu.
For Chinese music devotees, i.e. those with good education and cosmopolitan outlooks, Verdi existed on the printed page and, sometimes, on the gramophone player. Stories of Western Opera, written by Xu Chi, a renowned writer, was one of several such titles popular in Shanghai in the 1930s-40s. Liu Shirong has clear memory of attending a fan club in Chengdu in 1944 when he heard a record of Un Ballo in Maschera. While a music student in Chongqing, he also went to a group meeting where the complete Il Trovatore was played, with explanatory guidance from a fellow student.
Still, the 1956 La Traviata was a milestone, not only because it featured all Chinese artists, but because it happened at all in a heavily ideological climate. The main reason Verdi could be performed at all in the early years of New China was that the Italian composer was embraced in the Soviet Union. A Soviet soprano was coaching at the China National Opera House, and to the amazement of everyone around, she proposed doing La Traviata rather than a Russian opera. "She had played the leading role in Moscow, and she showed us glamorous photos of it," recollects Liu.
Li Guangxi, who initiated the role of Alfredo Germont in New China, sang the opera from 1956 to 1963, and then after the "cultural revolution" (1966-76), from 1979 to 1984. Using the original French La dame aux Camelias as the Chinese title, the opera was so popular that during a 1962 run in Shanghai, it filled a 2,400-seat theater for 20 nights, with the ticket-buying line stretching for hundreds of meters along the street. The 1979 tour of Tianjin, saw the opera performed 39 times in a 2,300-seat theater.
La Traviata was also the first Western opera to be revived in post-"cultural revolution" China, later followed by Rigoletto, Il Trovatore and many of Verdi's middle-age work. But for the masses with little access to the occasional theatrical performance, the availability of the videodisk around 1990 was a watershed in raising the exposure to — and level of appreciation for — Verdi and other Western musicians. There are accounts of opera-curious youths bicycling across Beijing to attend screenings of the 1983 film version of La Traviata directed by Franco Zeffirelli and starring Domingo. Though using an informal venue with disregard to authorization, the run was said to be much longer than most blockbusters of today.
"In the old days, only China National Opera House was allowed to do Western operas," explains Liu. "But now anyone can produce one, and the first choice is usually a Verdi work. It is simply more popular with the public." Compared with Wagner, for example. Though there is no data, empirical evidence shows that Chinese music fans would prefer Verdi over Wagner, but those who love Wagner tend to be intensely loyal, something akin to "religious fervor" in the words of music critic Tang Ruofu. Some experts explain that the Chinese singing tradition of "one singing followed by three others" is reminiscent of the structure in a typical Verdi aria and cabaletta. That and the hummable vocal lines have made Verdi much beloved by a wider swath of China's music-loving society.
For those who want to check out the scores, some of Verdi's manuscripts are on display in the China National Museum, or they can go to NCPA for its extravagant productions. So far, it has done La Traviata, Un Ballo, Otello, Nabucco, Rigoletto and, in concert form, Aida. "Nobody beats NCPA in China in the scale of a production," says Li Cheng, an opera critic. "But it is a giant standing on the shoulder of previous generations." One of these pioneers is Qian Shijin, who presented the China premieres of several Verdi works in Shanghai.
Li cites spinto soprano He Hui as a major Chinese proponent for Verdi. After making rounds of the world's greatest opera houses, she returned to China in Un Ballo and Aida, wowing her home audience with superlative delivery of Verdian grandeur.
Related Stories
Beijing Music Festival salutes Verdi and Wagner 2013-09-27 07:09
Shining a spotlight on Verdi and Wagner's legacies 2013-09-27 07:09
Original is best for Wagner's bicentenary 2013-07-05 07:22
Best of Wagner, Verdi 2013-03-22 11:12
Today's Top News
Mayor of Nanjing under probe
FDI rose 4.88% in September
Former mistresses are active online whistle-blowers
Guardian star reporter leaves for 'dream' project
Quantum of solace as breakthrough looms
London mayor hails China's FTZ, subway
Deal passed to end US debt crisis
China has record number of billionaires
Hot Topics
Lunar probe , China growth forecasts, Emission rules get tougher, China seen through 'colored lens', International board,
Editor's Picks

|

|

|
|

|

|





