Beware of capital account liberalization
Updated: 2015-05-22 08:05
By Zhang Ming(China Daily Europe)
|
|||||||||||
Where there is haste there is also a great risk of unintended consequences
The International Monetary Fund is going to reevaluate the currency basket of Special Drawing Rights this year, and one of the options is to include the renminbi in the basket. Christine Lagarde, president of the IMF, says China should further speed up the capital account liberalization to achieve this goal.
In March, during the annual sessions of the National People's Congress, the state legislature, and the advisory Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, a leader of the People's Bank of China reaffirmed that China would essentially realize the goal of the capital account liberalization by the end of this year.
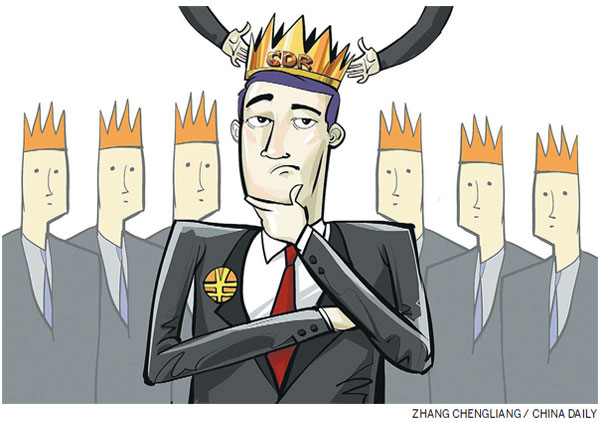

It would be good if China could join the SDR club. It would mark the renminbi as an international currency, accepted by the IMF, an international multilateral financial institution. However, becoming an SDR member does not mean that significant achievements have been made in internationalizing the renminbi.
The SDR, established in the early 1970s, has played a limited role. It only applies to the official settlement between the IMF and member countries, and it is not widely used for pricing or settlement in the global financial market. In other words, even if the RMB joins the SDR, the symbolic meaning is deeper than its practical implications.
A currency must meet two standards to qualify for the SDR. The first is that the issuing country occupies an important position in the global economy, which China has achieved by becoming the world's second-largest economy and the world's largest trading nation. The second is that the currency, in this case the renminbi, should be used widely and internationally. The definition of this is vague. The widespread use of the international currency does not necessarily mean the full liberalization of capital accounts, but in the eyes of the market and policymakers, the two things seem to amount to the same thing.
Since 2012, China has organized academic discussions on whether the government should speed up the liberalization of capital account. The main point is not whether it should be liberalized, but whether the process should be accelerated. At the Research Center for International Finance, part of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences' Institute of World Economics and Politics, we hold a sharp negative attitude. We are concerned that an acceleration could lead to massive capital outflows, which could be detrimental to China's macroeconomic and financial market stability, and may even hamper or harm domestic structural reforms.
Several years on and the discussion on whether to speed up the process has already exerted a certain influence on some policies. Even the leader of the People's Bank of China declared that China will accelerate capital account convertibility, but at the same time he also reiterated the need to strengthen monitoring and management of short-term capital flows. In other words, speeding up does not mean completely abandoning control over short-term capital movement.
This stance is commendable. However, during the two sessions this year, the central bank's saying that the capital account will essentially be liberalized by the end of this year, and facilitate the renminbi joining the SDR basket by speeding up capital account liberalization once again gave cause for a great deal of concern.
Speeding up capital account liberalization may still lead to increased volatility of short-term international capital. Consequently, it may intensify domestic financial risks explicitly, even embedding hidden dangers. It would be handy to look at the consequences of speeding up capital account liberalization, from both an international and a domestic perspective.

From an international perspective, the European Central Bank introduced new quantitative easy monetary policies in March, and the Central Bank of Japan is maintaining the loosest monetary policy in its history, but the focus of the global policy is still normalization of United States monetary policy. In October, the Federal Reserve had completely withdrawn from the quantitative easy monetary policy. From some time this year, the Fed is likely to enter a new round of the interest-rate rise cycle, which will dampen global investors' appetite for risk, causing global investors to increase their holding of dollar-denominated assets. As a result, huge sums of short-term international capital will flow from emerging market countries to the US and other developed countries.
From the domestic perspective, as China's economic growth potential declines, the financial risks are increasingly explicit. Against the background of weakened demand at home and abroad, the issue of seriously increasing overcapacity will result in the corporate sector deleveraging. Meanwhile, although the Chinese government has recently started to ease credit policies, it cannot reverse the trend of the real estate market's downward adjustment. The inevitable result is that China's non-performing loans in the banking system will be significantly increased in the years to come.
In addition, the Chinese government's plan to establish deposit insurance corporations this year will transform implicit insurance into explicit insurance for financial institutions, meaning some small and medium-sized financial institutions will be allowed to fail. With this is mind, confidence in the country's financial system will be reduced significantly.
For analysis it is not difficult to see China is facing a rising probability of capital outflow. If the government speeds up capital account liberalization, the economy is likely to face sustained, massive short-term capital outflows, which will have two negative impacts: Increased expectations that the renminbi falling in value, which will further deepen capital outflows and form a vicious circle, and tightened domestic liquidity. If the central bank cannot intervene in time, domestic interest rates will be raised significantly.
There are two schools of thought. One is that if there is sustained massive short-term capital outflow, the central bank may tighten capital controls again. However, that will not only damage the reputation of the central bank, but be costly and may cause turbulence in macroeconomic and financial markets.
The other is that China has nearly $4 trillion in foreign exchange reserves, enough to deal with massive capital outflows. Although China's M2 to GDP ratio is close to 200 percent, its foreign exchange reserves may shrink significantly, which will deepen investor concerns.
The internationalization of the renminbi should be a natural result of China's sustained and rapid economic growth and its financial market development and growth. Before achieving these goals, we should promote domestic structural reforms and avoid a systemic crisis.
Speeding up capital account liberalization has no real benefit for the policies of structural reform, such as domestic income redistribution and breaking the monopoly of State-owned enterprises. But an acceleration may set off a crisis. Further opening of the capital account should be done with caution.
The government should first accelerate the reform of the renminbi exchange rate and interest rate formation mechanism, and the establishment of the macro-prudential regulation framework. Otherwise, China risks going through what Russia went through last year: it had a spurt of capital outflows, and the rouble depreciated markedly against the US dollar, which forced its central bank to raise interest rates significantly.
The author is senior research fellow and head of the department of international investment at the Institute of World Economics and Politics, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. The views do not necessarily reflect those of China Daily.
(China Daily European Weekly 05/22/2015 page10)
Today's Top News
Premier Li urges harnessing China's manufacturing prowess
OPEC turn down Chinese requests for extra oil
Beijing concerned as US accuses 6 Chinese of economic spying
Ma backs female entrepreneurs
China, Brazil launch new era of economic relations
China jumps 28 positions in global tourism competitiveness ranking
Xiaomi debuts in US, Europe with online store
Milan Expo highlights need to ensure healthy, safe, sufficient food for all
Hot Topics
Lunar probe , China growth forecasts, Emission rules get tougher, China seen through 'colored lens', International board,
Editor's Picks

|

|

|

|
|

|






