Salary bonanza for bosses
Updated: 2011-09-09 15:45
By Ben Yue (China Daily)
Top boss gets 8.78 million euros a year, far more than the State enterprise CEO with highest pay

Yang Yuanqing, chief executive officer of Lenovo Group, in a Zhongguancun street in Beijing's Haidian district. His company's headquarters were located there in the 1980s with the staff crowded in a dusty old building sited behind him in what is now a bustling street corner. As the company became a multinational business, Yang's annual income rose to its current 78.72 million yuan, equal to the annual revenue of a medium-sized Chinese company. [Provided to China Daily]
China's highest paid executive this year is Yang Yuanqing, CEO of Lenovo Group. His annual salary of 78.72 million yuan (8.78 million euros) is equivalent to that of 24 top United States executives after the US government sought to limit some CEOs' annual salaries there to $500,000 in 2009 during the recovery from the financial crisis.
Following the US policy, China also placed limits on salaries in 2009 - 2.8 million yuan for executives of State-owned enterprises (SOEs) - but the policy seems to have been ignored, according to the newly released Forbes' CEO salary rankings of Chinese-listed companies.
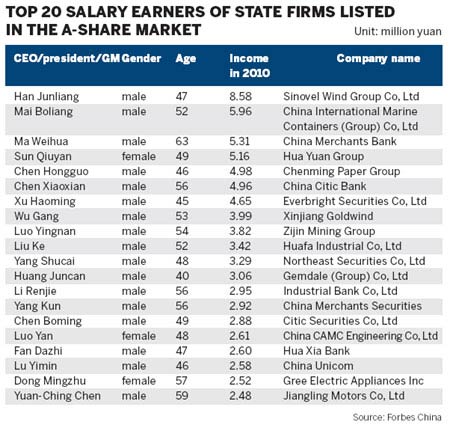
The highest paid CEO at an SOE is Han Junliang, who was paid 8.58 million yuan by Sinovel Wind Group Co Ltd this year.
The highest paid CEO in the A-share market (yuan-denominated shares on the Chinese mainland) is Ma Mingzhe, CEO of private company Ping An Insurance (Group) Company of China Ltd, who received 9.87 million yuan.
Yang Yuanqing is the highest paid in the H-share market (Hong Kong-listed shares of mainland companies), with a salary almost eight times higher than that of Ma Mingzhe.
According to the list, there are 232 A-share market CEOs whose annual salary exceeds 1 million yuan, of whom 121 of them are from SOEs and the other 111 from private companies.
About half of these CEOs work in the finance, IT, real estate, energy and pharmaceutical industries.
"Executives in China change jobs less frequently than the global norm and these listed companies are doing well," says Jennifer Feng, 51job.com's chief human resources expert. "About 70 percent of listed companies saw 15 percent to 20 percent growth last year, which is much higher than China's GDP growth."
She says some of these companies' good performances do not necessarily reflect the good performances of their top executives. SOEs, for example, are naturally positioned comfortably in the market and enjoy favorable policies.
"The payments of CEOs do not just depend upon their performances. It's also decided by the market," says Feng. "Besides, as these CEOs are managing billions in assets, payment below 1 million yuan could affect their effort in the workplace."
The high salaries of listed-company executives have been the subject of much debate in recent years in China because the income gap between the wealthy and other classes is growing.
A report released in 2010 by the All-China Federation of Trade Unions showed that SOE executives earned on average 18 times the average salary of their employees. About 20 percent of these employees' salaries have not risen in the past two years.
However, Feng says the main point of the dispute over executives' salaries is not about whether CEOs are getting too much. "It is about whether the individual investors are getting too little from these companies' good performances."
According to Feng, CEOs all around the world are paid well but, in the US, individual investors share the profits with the executives. "In China, the main purpose of companies going public is for financing. Some companies have not distributed dividends for five years although they are expanding their businesses fast."
Zhang Juwei, deputy director of the Institute of Population and Labor Economics under the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, says the government should set a long-term mechanism to limit the salary of SOE executives even if the companies are performing extremely well.
"These executives are not recruited from the market but assigned by the government. Many huge SOEs have important social functions to provide welfare to society, such as energy and transportation," says Zhang. "Paying too much will also affect the performance of civil servants who do a similar job to the SOE executives."
Zhang suggests imposing limits on the salary of SOE executives based on the salaries of civil servants at an equivalent level.
Data from the Forbes report shows 121 A-share SOEs which paid more than 1 million yuan to their CEOs had a combined growth rate of 33 percent on sales and 47 percent growth on net profits in 2010.
The government has allowed SOE executives to hold and sell a small percentage of their companies' shares since 2005 and released details regulations in 2006.
"Because the policy required conditional selling periods, some SOE executives call it 'paper wealth'," says Feng.
She also says that Chinese CEOs are not ready to take a $1 annual salary as Steve Jobs of Apple Inc and John Chambers of Cisco Systems Inc did 10 years ago to help their companies out of trouble.
"The CEOs in Western countries take a nominal salary while their major personal assets are shares and options. This is hard to transplant to China because we have so many SOEs," Feng says. "But I do think Chinese companies have a lot to learn from the way Western companies reward their executives."
E-paper

Way over the moon
After an outcry several years ago about wasteful packaging, it seems that the mooncake makers of China have seen the light.
From death matches to child's play
Tomb raiders remain a menace
Kicking for joy
Specials

China at her fingertips
Veteran US-China relations expert says bilateral ties have withstood the test of time

The myth buster
An outsider's look at china's leaders is updated and expanded

China in vogue
How Country captured the fascination of the world's most powerful fashion player
