All-round reform on the agenda
Updated: 2013-11-08 08:12
(China Daily)
|
|||||||||||
1988 9.26-9.30
13th CPC Central Committee
Price and salary reform
China was at a transition point between two economic systems and underwent a turbulent economic situation and surging prices. In order to deepen reform and opening-up, the meeting formulated guidelines to improve the economic environment and rectify the economic structure.
1990.11.26
The Shanghai Stock Exchange was founded, the first on the Chinese mainland since 1949, followed by the establishment of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange five days later. At the end of last year, Shanghai was ranked seventh in the world by market capitalization, while Shenzhen was 16th.
1993 11.11-11.14
14th CPC Central Committee
Plan for systemic market reform
The plenum declared the intention of building a socialist market economy system. Under such a system, the market plays a fundamental role in resource allocation within the context of State macro-adjustment and control. The meeting also ordered all State-owned enterprises to reform their operations, establish modern enterprise mechanisms to clearly define property rights, separate ownership from day-to-day management and adopt scientific management methods.
1993.12.15
The State Council decided to reform the country's fiscal management and implement a new revenue-sharing system in favor of the central government.
1994.1
China unified its dual exchange rates by aligning official and swap center rates, officially devaluing the renminbi overnight by 33 percent to 8.7 to the US dollar.
1994.7.18
A new policy was issued to deepen reform of the urban housing system, which initiated the commercialization of urban housing.

1997
This year witnessed the birth of several Chinese Internet start-ups, including NetEase, and ITC, the predecessor of Sohu. Lenovo overtook IBM to become the top-selling computer company in China.
1998 10.12-10.14
15th CPC Central Committee
Building a new socialist countryside
The session set the goal of building a new socialist countryside by 2010, outlined targets for agricultural and rural development and issued strategies and policies on economic, political and cultural construction in rural areas. Along with rapid industrialization and urbanization, developmental imbalances had seen the urban-rural wealth gap widen. The blueprint reflected the Party's understanding of the need to strengthen rural reform and development.
1999.3.22
The State Council stipulated 10 measures for the further development of China's western region. From 1999 to 2009, the central government provided more than 3.5 trillion yuan to support the development of the region, resulting in 9.54 million rural residents being lifted out of poverty in the western region.
2001.12.11

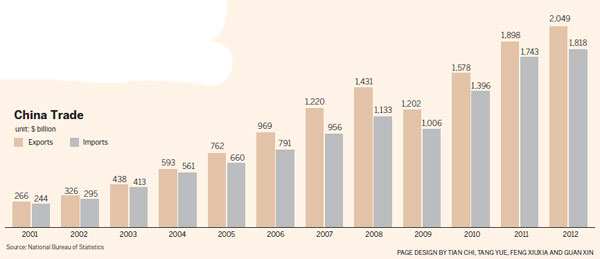
China became a member of the World Trade Organization after 15 years of negotiation. In 2012, the country's total import and export volume amounted to $3.86 trillion. China is expected to replace the US as the world's largest trading nation by the end of this year.
2003 10.11-10.14
16th CPC Central Committee
Scientific OUTLOOK ON development
The plenum encouraged a scientific outlook on development with "five balances": Urban and rural development; development among regions; economic and social development; man and nature; and domestic development and opening-up to the outside world.
2004.3.14

Protection of private property and human rights were written into the Chinese Constitution as the fourth Constitutional Amendment was passed. The amendment stated: "Citizens' legal private property should not be infringed upon" and "The State respects and protects human rights". The Property Law came into effect on Oct 1, 2007.
2005.12.19
The agriculture tax was abolished, relieving more than 800 million farmers of the need to pay it.
2008 10.9-10.12
17th CPC Central Committee
Further rural reform
A blueprint for rural reform by 2020 was released. It aimed to accelerate the construction of a new socialist countryside and accelerate the overall development of urban and rural areas.
2008.11.9
Faced with the global financial crisis, China released a 4-trillion-yuan stimulus package to finance programs including infrastructure, low-income housing, medical services and social welfare. Despite the package, more than 20 million migrant workers lost their jobs as a result of the financial crisis.
2010
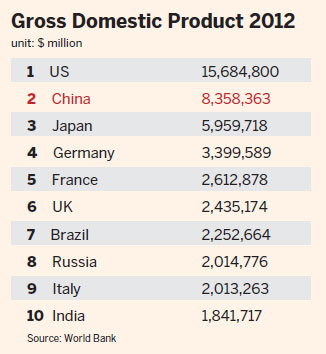
China overtook Japan to become the world's second-largest economy.
Related Stories
June 6—9, 1950: The Third Plenary Session of the Seventh CPC Central Committee is held in Beijing 2011-06-07 15:52
CPC members told to think of the people 2013-09-30 10:56
CPC's time-honored tradition still crucial to rural development 2013-08-24 14:52
Today's Top News
Russian meteor studied for clues to next one
China's increasing role in global nuclear power
Registration eased for foreign firms
CIA paying AT&T to provide call records - NY Times
Twitter soar 92% in NYSE debut
Li promises reasonable growth rate
Possible evidence of Arafat poisoning
Sex education cartoon an instant online hit
Hot Topics
Lunar probe , China growth forecasts, Emission rules get tougher, China seen through 'colored lens', International board,
Editor's Picks

|

|

|

|

|

|






