Yunnan brews up cups of success
Updated: 2013-06-26 08:41
By Hu Yongqi (China Daily)
|
|||||||||||
|
 |
|
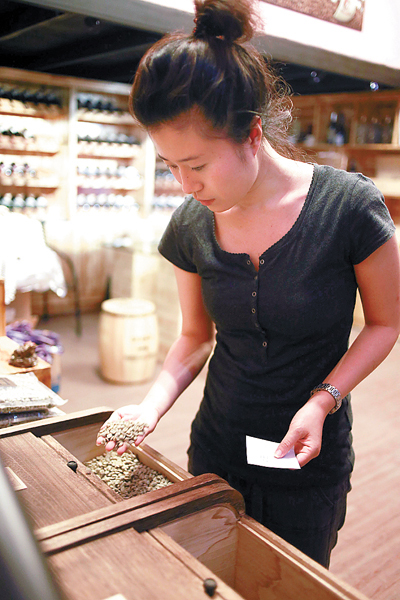
Xing Wanbin, the wife of Jin Jihui, the manager of One Percent Coffee Co in Pu'er, selects beans in Pu'er. [Photo by Feng Yongbin/China Daily] |
Yunnan tops the list of China's three major coffee-growing areas, producing more than 95 percent of the country's crop. In Pu'er, which has a population of 2.36 million, the area of land devoted to coffee was increased by 30 percent to 43,000 hectares in 2011 and 2012.
Coffee has bought Shi's family a two-story house and two cars and even though the price per kg has seen wide fluctuations in the past five years, he has no intention of quitting the business. In 2011, the highest price paid for a kg of coffee was 40 yuan, but that has fallen to 16 yuan this year. Shi made 400,000 yuan in 2011, but last year his income dropped to 80,000 yuan.
"You can't cut down all the coffee trees when the beans don't fetch a good price. Patience is needed to bear the ups and downs," said Jiang Jirong, 52, another Dakaihe resident and coffee farmer.
Experts, such as Sheng Jun, president of Yunnan Agriculture University, and coffee manufacturers said the coffee futures market fundamentally controls prices and farmers must find a way to avert the risks with the aid of the local government.
Pu'er is famous for its tea, and the two are synonymous in the eyes of many Chinese. However, the city's natural environment - a huge swing in temperature between day and night, high levels of rainfall and adequate sunshine - is not only perfect for the cultivation of tea, but also for coffee.
Dakaihe was once a byword for poverty. The limited amount of land in the village in the late 1980s meant locals couldn't grow enough rice to feed their families, so when Shi sold his beans for 28 yuan per kg in 1992, his neighbors were envious and scrambled to grow coffee on their land.
Now, each household grows about 3.5 hectares of coffee on average. In the village, coffee trees, blooming in the mid-June sunlight, stand in neat rows across the small hills, covering about 340 hectares. Consequently, the average net income has reached 15,000 yuan, three times the average in Pu'er.
Business was boosted in 1989 when Nestle, the Swiss food and drinks group, began to buy coffee beans grown in Pu'er. At the time, small Arabica coffee beans dominated Pu'er's farms, accounting for more than 90 percent of the area under cultivation. Coffee businesses targeted potential consumption in China, boosting production in Pu'er and other areas in Yunnan, such as the Dehong Dai and Jingpo autonomous prefecture and Baoshan city.
"The traditional beverage - tea - is popular among the middle-aged and elderly. In many cities nowadays, the pace of life has changed, everything is done so quickly and the younger generation don't have time to elegantly make tea. They prefer coffee. People are changing their habits," said Jin Jihui, general manger of One Percent Coffee Co, based in Pu'er.
Last year, coffee consumption in emerging markets such as China and Russia rose by 10 percent, according to the London-based International Coffee Organization.
Jin said the coffee he drank on his first visit to Pu'er five years ago attracted him to stay in the small city and start his own business. He registered a company in January and will soon establish a factory in the suburbs.
In 2006, Pu'er coffee was awarded 88.75 points out of 100 by the Specialty Coffee Association of America, the world's largest coffee trading organization, while coffee from Colombia, one of the world's best-known producers, earned 85.88 points.
In June 2012, the Pu'er city government established the Coffee Industry Development Office, China's only county-level office dedicated to the management of plantations and coffee production. The main job of the office is to promote local products to the coffee professionals who are focusing on the Chinese market.
"Our coffee is of superb quality. Pu'er aims to become a major distribution center for China and Southeast Asian countries," said Lu Han, director of Pu'er Coffee Industry Development Office.
Sheng Jun said: "Coffee has been planted in Pu'er city for more than 100 years, having been introduced by French missionaries in 1902. Since the 1980s, coffee has been planted on a large scale. At present, the cultivated area for Pu'er tea is 240,000 hectares, almost six times that for coffee."
Hoping to ride the rising wave of popularity, the city government has stipulated that the coffee plantation will be expanded to 66,600 hectares by 2016, and no new land will be allocated for tea.
Related Stories
Yunnan cultural trade center opens in Singapore 2013-06-25 17:03
Yunnan promotes tourism in Kuala Lumpur 2013-06-25 17:03
Cross-border RMB settlement surges in Yunnan 2013-06-07 16:59
Communication essential for Yunnan chemical project 2013-05-18 02:01
Increased tourism to Yunnan ahead of Songkran Festival 2013-04-10 17:25
Today's Top News
France wants more Chinese investment
FM: China rejects US' claim on Snowden
Public interests Party's top priority
Overseas sellers upbeat on China
PBOC will act 'if necessary'
4 Chinese killed in Papua New Guinea
'Heavy losses' if China-EU solar sector talks fail
Riots in Xinjiang kill 27
Hot Topics
Lunar probe , China growth forecasts, Emission rules get tougher, China seen through 'colored lens', International board,
Editor's Picks

|
|

|

|

|

|





